StarTree
Querying Overview
StarTree is a SQL oriented database based on Apache Pinot. For details on Apache Pinot see https://docs.pinot.apache.org/. StarTree includes support for JSON data and vector searches as discussed in more detail below.
SQL Queries
Apache Pinot provides a SQL interface for querying. It uses the Calcite SQL parser to parse queries and the MYSQL_ANSI dialect. For details on the syntax, see
https://calcite.apache.org/docs/reference.html
Qarbine generally passes along your SQL query as-is to the StarTree backend using StarTree’s RESTful service endpoint. Qarbine provides several virtual queries which are described in the DBA Productivity related document and also convenient answer set pragmas described in the Data Source Designer guide.
When querying a StarTree database using the REST API, the default number of rows returned is typically 10. This default behavior can be overridden by specifying a LIMIT clause in your query to adjust the number of rows returned.
For StarTree answer sets Qarbine automatically converts non null values for the data types listed below.
| Data Type | Automatic Conversion |
|---|---|
| timestamp | Date object |
| JSON | JSON object |
| Boolean | A true or false value |
For more details see
https://docs.pinot.apache.org/users/user-guide-query
StarTree provides query options as described at the following link
https://docs.pinot.apache.org/users/user-guide-query/query-options
These options are global in nature and set by the Qarbine administrator when the StarTree associated data service is defined.
Explaining Queries
StarTree provides an EXPLAIN query feature. A sample query is shown below.
EXPLAIN PLAN FOR
select *
from myComplexWebSite
order by country, clicks desc
limit 25
Sample output is shown below.
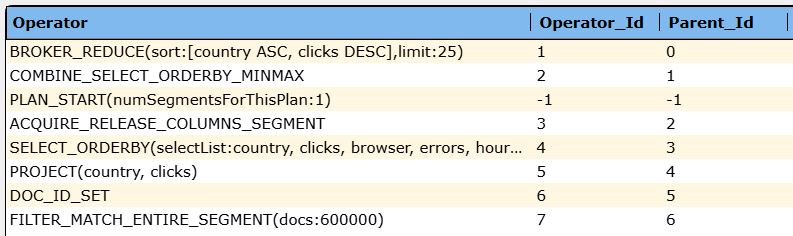
For more details see
https://docs.pinot.apache.org/users/user-guide-query/query-syntax/explain-plan
Remember you can easily comment out query specification lines using the “//” syntax.
// EXPLAIN PLAN FOR
select *
from myComplexWebSite
order by country, clicks desc
limit 25
Handling JSON Data
Overview
As a SQL oriented database any JSON data is generally returned in its string form by legacy tools. For JSON with even just a few fields, this can be a burden for analysis tasks. StarTree does have SQL functions to extract individual values, but this immediately adds a column to the result set as well. As the JSON structure starts to even get mildly complex or even nested, the use of these functions greatly impacts the answer set shape and size.
Qarbine automatically coerces JSON data types into JSON objects for analysis. End users, analysts, and developers do not have to write code to turn the strings into real JSON objects.
Details on StarTree’s JSON handling can be found at
https://dev.startree.ai/docs/pinot/recipes/json-index
General Apache Pinot JSON handling details can be found at
https://docs.pinot.apache.org/users/user-guide-query/query-syntax/json-queries
Using Pragmas for JSON Data
Below are a few of the pragmas from the general Qarbine Data Source Designer guide to consider using with the StarTree JSON data.
| Pragma Keyword | Description |
|---|---|
| deleteFields | Provide a CSV list of fields to delete. The arguments may have field paths of up to 2 levels. The first level can be a document or an array of documents. The deleting is done in-place. This is convenient when the result row/document has many fields and you want all just a few of them. Rather than explicitly list the 20 say fields of the 23, just ‘delete’ those 3 from the answer set. |
| pullFieldsUp | Provide a CSV list of object fields to pull their contents up to the first level. The original field is deleted. This can be useful when there are many inner fields that can be part of the first level. Instead of several template formulas like #container.first and #container.last you can simply use #first and #last via the line#pragma pullFieldsUp container |
The pragmas are generally placed above the StarTree SQL query.
Timestamp Handling
StarTree has a timestamp data type. Qarbine automatically converts these column values into date objects.
StarTree also provides several functions for interacting with timestamps stored as numbers or strings. Most result in either a milliseconds epoch value or a formatted date string. Such values can be converted into real Date objects using the Qarbine line “#pragma convertToDate fieldNamesCSV”.
For more details see
https://dev.startree.ai/docs/use-data-manager/recipes/mapping-functions#datetime-functions
Vector Queries
Overview
StarTree supports vector similarity searches as well. Remember that to perform a similarity search, you need to use the same model to generate an embedding for your query as was used to generate the stored embeddings in the database. For details see https://dev.startree.ai/docs/pinot/concepts/vector-search#introduction.
Vector Functions
The StarTree clause supporting vector searches has the structure
VECTOR_SIMILARITY(v1, v2, [topK] )
| Parameter | Comment |
|---|---|
| v1 and v2 | Represents a floating point vector. You can reference a Pinot column here as well. |
| topK | Optionally specifies how many topK values to return. It accepts positive integer values. The default is 10. |
An example vector search query is:
SELECT ProductId, UserId, combined, n_tokens
l2_distance(embedding, ARRAY[-0.001314,-0.011049,...]) AS l2_dist
FROM fineFoodReviews
WHERE VECTOR_SIMILARITY(embedding, ARRAY[-0.001676,-0.011099,...], 5)
ORDER by l2_dist ASC
LIMIT 10
There are several other helpful scalar functions that can be helpful.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| COSINE_DISTANCE | Returns the cosine distance between two vectors, with a default value if the norm of either vector is 0. |
| L1_DISTANCE | Returns the L1 distance (Manhattan distance) between two vectors. |
| L2_DISTANCE | Returns the L2 distance (Euclidean distance) between two vectors. |
| INNER_PRODUCT | Returns the inner product between two vectors. |
Here is an example using the cosine distance function.
SELECT name, cosine_distance(vector, [0.2, -0.1, 0.3, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2, ]) AS similarity
FROM myVectors
ORDER BY similarity DESC
LIMIT 5
For details see this link,
https://dev.startree.ai/docs/pinot/concepts/vector-search
and https://dev.startree.ai/docs/pinot/concepts/vector-search#executing-similarity-search-queries.
A link to a vector oriented tutorial is https://github.com/startreedata/pinot-recipes/tree/main/recipes/vector.
Troubleshooting
If there is a query which returns unexpected results then first cross reference the results using the standard online StarTree Query Console. For details see
https://dev.startree.ai/docs/query-data/query-using-console
After logging in you can access the console using the button shown below.
Also check the health of your StarTree database based on the documentation at https://dev.startree.ai/docs/reference/use-cluster-health-dashboard
In the Data Source Designer pressing Alt and clicking the run image returns the effective query that would be sent to StarTree. This query has had all variables and macro functions evaluated by this point.